Popular Libraries
Scikit-Learn
Get Historical Data
Get some historical market data to train and test the model. For example, to get data for the SPY ETF during 2020 and 2021, run:
qb = QuantBook()
symbol = qb.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol
history = qb.history(symbol, datetime(2020, 1, 1), datetime(2022, 1, 1)).loc[symbol]
Prepare Data
You need some historical data to prepare the data for the model. If you have historical data, manipulate it to train and test the model. In this example, use the following features and labels:
| Data Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Features | Daily percent change of the open, high, low, close, and volume of the SPY over the last 5 days |
| Labels | Daily percent return of the SPY over the next day |
The following image shows the time difference between the features and labels:
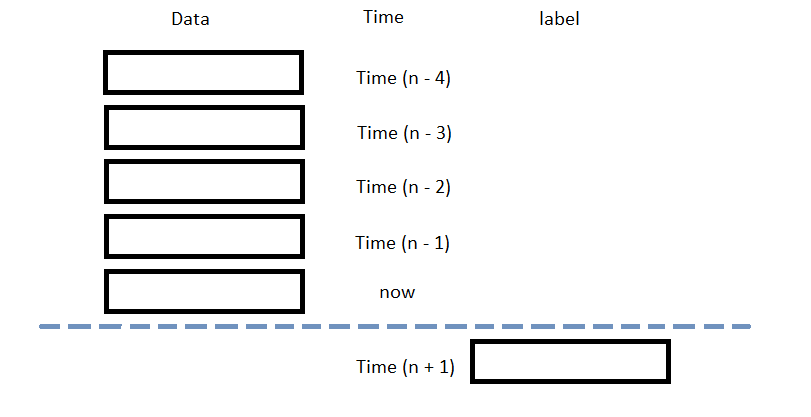
Follow these steps to prepare the data:
- Call the
pct_changemethod and then drop the first row. - Loop through the
daily_returnsDataFrame and collect the features and labels. - Convert the lists of features and labels into
numpyarrays. - Split the data into training and testing periods.
daily_returns = history['close'].pct_change()[1:]
n_steps = 5
features = []
labels = []
for i in range(len(daily_returns)-n_steps):
features.append(daily_returns.iloc[i:i+n_steps].values)
labels.append(daily_returns.iloc[i+n_steps])
X = np.array(features) y = np.array(labels)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
Train Models
You need to prepare the historical data for training before you train the model. If you have prepared the data, build and train the model. In this example, build a Support Vector Regressor model and optimize its hyperparameters with grid search cross-validation. Follow these steps to create the model:
- Set the choices of hyperparameters used for grid search testing.
- Call the
GridSearchCVconstructor with the SVR model, the parameter grid, a scoring method, the number of cross-validation folds. - Call the
fitmethod and then select the best estimator.
param_grid = {'C': [.05, .1, .5, 1, 5, 10],
'epsilon': [0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1],
'gamma': ['auto', 'scale']}
gsc = GridSearchCV(SVR(), param_grid, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=5)
model = gsc.fit(X_train, y_train).best_estimator_
Test Models
You need to build and train the model before you test its performance. If you have trained the model, test it on the out-of-sample data. Follow these steps to test the model:
- Call the
predictmethod with the features of the testing period. - Plot the actual and predicted labels of the testing period.
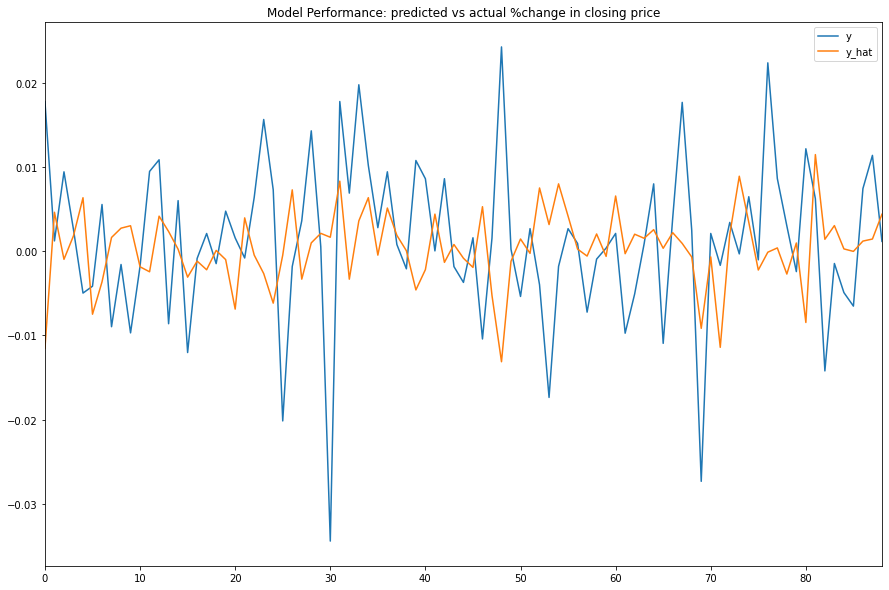
y_hat = model.predict(X_test)
df = pd.DataFrame({'y': y_test.flatten(), 'y_hat': y_hat.flatten()})
df.plot(title='Model Performance: predicted vs actual %change in closing price', figsize=(15, 10))
Store Models
You can save and load sklearn models using the Object Store.
Save Models
Follow these steps to save models in the Object Store:
- Set the key name of the model to be stored in the Object Store.
- Call the
GetFilePathget_file_pathmethod with the key. - Call the
dumpmethod with the model and file path.
model_key = "model"
file_name = qb.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
This method returns the file path where the model will be stored.
joblib.dump(model, file_name)
If you dump the model using the joblib module before you save the model, you don't need to retrain the model.
Load Models
You must save a model into the Object Store before you can load it from the Object Store. If you saved a model, follow these steps to load it:
- Call the
ContainsKeycontains_keymethod with the model key. - Call
GetFilePathwith the key. - Call
loadwith the file path.
qb.object_store.contains_key(model_key)
This method returns a boolean that represents if the model_key is in the Object Store. If the Object Store does not contain the model_key, save the model using the model_key before you proceed.
file_name = qb.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
This method returns the path where the model is stored.
loaded_model = joblib.load(file_name)
This method returns the saved model.
Examples
The following examples demonstrate some common practices for using the sklearn library.
Example 1: Predict Next Return
The following research notebook uses sklearn machine learning model to predict the next day's return by the previous 5 days' daily returns.
# Import the sklearn library and others.
from sklearn.svm import SVR
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import joblib
# Instantiate the QuantBook for researching.
qb = QuantBook()
# Request the daily SPY history with the date range to be studied.
symbol = qb.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol
history = qb.history(symbol, datetime(2020, 1, 1), datetime(2022, 1, 1)).loc[symbol]
# Obtain the daily returns to be the features and labels.
daily_returns = history['close'].pct_change()[1:]
# We use the previous 5 day returns as the features to be studied.
# Get the 1-day forward return as the labels for the machine to learn.
n_steps = 5
features = []
labels = []
for i in range(len(daily_returns)-n_steps):
features.append(daily_returns.iloc[i:i+n_steps].values)
labels.append(daily_returns.iloc[i+n_steps])
# Split the data as a training set and test set for validation.
features = np.array(features)
labels = np.array(labels)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
# Set the choices of hyperparameters used for grid search testing.
param_grid = {'C': [.05, .1, .5, 1, 5, 10],
'epsilon': [0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1],
'gamma': ['auto', 'scale']}
# Call the GridSearchCV constructor with the SVR model, the parameter grid, a scoring method, the number of cross-validation folds.
gsc = GridSearchCV(SVR(), param_grid, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=5)
# Call the fit method and then select the best estimator.
model = gsc.fit(X_train, y_train).best_estimator_
# Call the predict method with the features of the testing period.
y_hat = model.predict(X_test)
# Plot the actual and predicted labels of the testing period.
df = pd.DataFrame({'y': y_test.flatten(), 'y_hat': y_hat.flatten()})
df.plot(title='Model Performance: predicted vs actual %change in closing price', figsize=(15, 10))
# Store the model in the object store to allow accessing the model in the next research session or in the algorithm for trading.
model_key = "model"
file_name = qb.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
joblib.dump(model, file_name)

