Datasets
Custom Data
Define Custom Data
You must format the data file into chronological order before you define the custom data class.
To define a custom data class, extend the BaseDataPythonData class and override the GetSource and Reader methods.
#load "../Initialize.csx"
#load "../QuantConnect.csx"
#r "../Microsoft.Data.Analysis.dll"
using QuantConnect;
using QuantConnect.Data;
using QuantConnect.Algorithm;
using QuantConnect.Research;
using Microsoft.Data.Analysis;
public class Nifty : BaseData
{
public decimal Open;
public decimal High;
public decimal Low;
public decimal Close;
public Nifty()
{
}
public override SubscriptionDataSource GetSource(SubscriptionDataConfig config, DateTime date, bool isLiveMode)
{
var url = "http://cdn.quantconnect.com.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/uploads/CNXNIFTY.csv";
return new SubscriptionDataSource(url, SubscriptionTransportMedium.RemoteFile);
}
public override BaseData Reader(SubscriptionDataConfig config, string line, DateTime date, bool isLiveMode)
{
var index = new Nifty();
index.Symbol = config.Symbol;
try
{
//Example File Format:
//Date, Open High Low Close Volume Turnover
//2011-09-13 7792.9 7799.9 7722.65 7748.7 116534670 6107.78
var data = line.Split(',');
index.Time = DateTime.Parse(data[0], CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
index.EndTime = index.Time.AddDays(1);
index.Open = data[1].IfNotNullOrEmpty<decimal>(s => decimal.Parse(s, NumberStyles.Any, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
index.High = data[2].IfNotNullOrEmpty<decimal>(s => decimal.Parse(s, NumberStyles.Any, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
index.Low = data[3].IfNotNullOrEmpty<decimal>(s => decimal.Parse(s, NumberStyles.Any, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
index.Close = data[4].IfNotNullOrEmpty<decimal>(s => decimal.Parse(s, NumberStyles.Any, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
index.Value = index.Close;
}
catch
{
// Do nothing
}
return index;
}
}
class Nifty(PythonData):
'''NIFTY Custom Data Class'''
def get_source(self, config: SubscriptionDataConfig, date: datetime, is_live_mode: bool) -> SubscriptionDataSource:
url = "http://cdn.quantconnect.com.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/uploads/CNXNIFTY.csv"
return SubscriptionDataSource(url, SubscriptionTransportMedium.REMOTE_FILE)
def reader(self, config: SubscriptionDataConfig, line: str, date: datetime, is_live_mode: bool) -> BaseData:
if not (line.strip() and line[0].isdigit()): return None
# New Nifty object
index = Nifty()
index.symbol = config.symbol
try:
# Example File Format:
# Date, Open High Low Close Volume Turnover
# 2011-09-13 7792.9 7799.9 7722.65 7748.7 116534670 6107.78
data = line.split(',')
index.time = datetime.strptime(data[0], "%Y-%m-%d")
index.end_time = index.time + timedelta(days=1)
index.value = data[4]
index["Open"] = float(data[1])
index["High"] = float(data[2])
index["Low"] = float(data[3])
index["Close"] = float(data[4])
except:
pass
return index
Create Subscriptions
You need to define a custom data class before you can subscribe to it.
Follow these steps to subscribe to custom dataset:
- Create a
QuantBook. - Call the
AddDataadd_datamethod with a ticker and then save a reference to the dataSymbol.
var qb = new QuantBook();
qb = QuantBook()
var symbol = qb.AddData<Nifty>("NIFTY").Symbol; symbol = qb.add_data(Nifty, "NIFTY").symbol
Custom data has its own resolution, so you don't need to specify it.
Get Historical Data
You need a subscription before you can request historical data for a security. You can request an amount of historical data based on a trailing number of bars, a trailing period of time, or a defined period of time.
Before you request data, call SetStartDateset_start_date method with a datetimeDateTime to reduce the risk of look-ahead bias.
qb.set_start_date(2014, 7, 29);
qb.set_start_date(2014, 7, 29)
If you call the SetStartDateset_start_date method, the date that you pass to the method is the latest date for which your history requests will return data.
Trailing Number of Bars
Call the Historyhistory method with a symbol, integer, and resolution to request historical data based on the given number of trailing bars and resolution.
var history = qb.history(symbol, 10);
history = qb.history(symbol, 10)
This method returns the most recent bars, excluding periods of time when the exchange was closed.
Trailing Period of Time
Call the Historyhistory method with a symbol, TimeSpantimedelta, and resolution to request historical data based on the given trailing period of time and resolution.
var history = qb.History(symbol, TimeSpan.FromDays(10));
history = qb.history(symbol, timedelta(days=10))
This method returns the most recent bars, excluding periods of time when the exchange was closed.
Defined Period of Time
Call the Historyhistory method with a symbol, start DateTimedatetime, end DateTimedatetime, and resolution to request historical data based on the defined period of time and resolution. The start and end times you provide are based in the notebook time zone.
var startTime = new DateTime(2013, 7, 29); var endTime = new DateTime(2014, 7, 29); var history = qb.History(symbol, startTime, endTime);
start_time = datetime(2013, 7, 29) end_time = datetime(2014, 7, 29) history = qb.history(symbol, start_time, end_time)
This method returns the bars that are timestamped within the defined period of time.
In all of the cases above, the Historyhistory method returns a DataFrame with a MultiIndex.
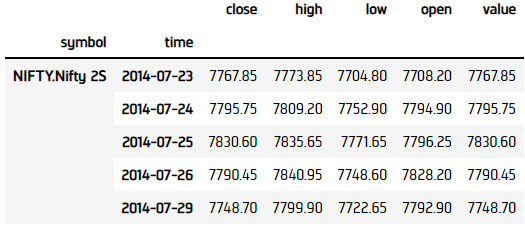
In all of the cases above, the Historyhistory method returns an IEnumerable<Nifty> for single-security requests.
Download Method
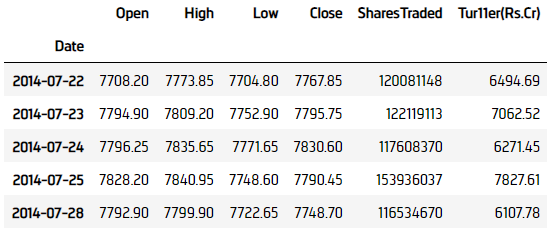
To download the data directly from the remote file location instead of using your custom data class, call the Downloaddownload method with the data URL.
var content = qb.download("http://cdn.quantconnect.com.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/uploads/CNXNIFTY.csv"); content = qb.download("http://cdn.quantconnect.com.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/uploads/CNXNIFTY.csv")
Follow these steps to convert the content to a DataFrame:
- Import the
StringIOfrom theiolibrary. - Create a
StringIO. - Call the
read_csvmethod.
from io import StringIO
data = StringIO(content)
dataframe = pd.read_csv(data, index_col=0)
Wrangle Data
You need some historical data to perform wrangling operations. To display pandas objects, run a cell in a notebook with the pandas object as the last line. To display other data formats, call the print method.
You need some historical data to perform wrangling operations. Use LINQ to wrangle the data and then call the Console.WriteLine method in a Jupyter Notebook to display the data.
The DataFrame that the Historyhistory method returns has the following index levels:
- Dataset
Symbol - The
EndTimeend_timeof the data sample
The columns of the DataFrame are the data properties.
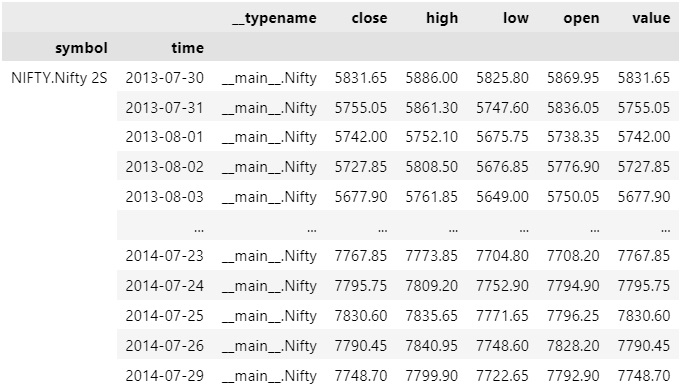
To select the data of a single dataset, index the loc property of the DataFrame with the data Symbol.
history.loc[symbol]
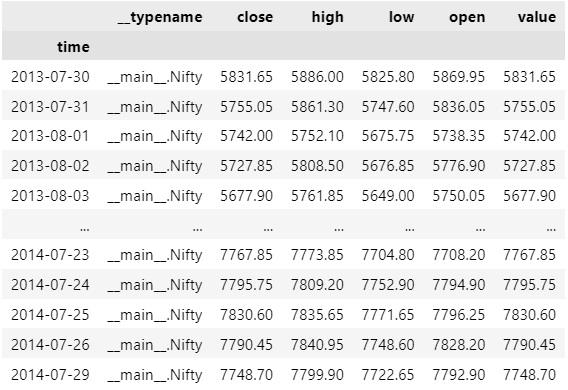
To select a column of the DataFrame, index it with the column name.
history.loc[symbol]['close']
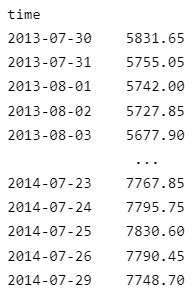
To get each custom data object, iterate through the result of the history request.
foreach(var nifty in history)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{nifty} EndTime: {nifty.EndTime}");
}
Plot Data
You need some historical custom data to produce plots. You can use many of the supported plotting librariesPlot.NET package to visualize data in various formats. For example, you can plot candlestick and line charts.
Candlestick Chart
Follow these steps to plot candlestick charts:
- Get some historical data.
- Import the
plotlyPlot.NETlibrary. - Create a
Candlestick. - Create a
Layout. - Create a
Figure. - Assign the
Layoutto the chart. - Show the
Figure.
history = qb.history(Nifty, datetime(2013, 7, 1), datetime(2014, 7, 31)).loc[symbol]
var history = qb.History<Nifty>(symbol, new DateTime(2013, 7, 1), new DateTime(2014, 7, 31));
import plotly.graph_objects as go
#r "../Plotly.NET.dll" using Plotly.NET; using Plotly.NET.LayoutObjects;
candlestick = go.Candlestick(x=history.index,
open=history['open'],
high=history['high'],
low=history['low'],
close=history['close']) var chart = Chart2D.Chart.Candlestick<decimal, decimal, decimal, decimal, DateTime, string>(
history.Select(x => x.Open),
history.Select(x => x.High),
history.Select(x => x.Low),
history.Select(x => x.Close),
history.Select(x => x.EndTime)
);
layout = go.Layout(title=go.layout.Title(text=f'{symbol} OHLC'),
xaxis_title='Date',
yaxis_title='Price',
xaxis_rangeslider_visible=False) LinearAxis xAxis = new LinearAxis();
xAxis.SetValue("title", "Time");
LinearAxis yAxis = new LinearAxis();
yAxis.SetValue("title", "Price ($)");
Title title = Title.init($"{symbol} OHLC");
Layout layout = new Layout();
layout.SetValue("xaxis", xAxis);
layout.SetValue("yaxis", yAxis);
layout.SetValue("title", title);
fig = go.Figure(data=[candlestick], layout=layout)
chart.WithLayout(layout);
fig.show()
HTML(GenericChart.toChartHTML(chart))
Candlestick charts display the open, high, low, and close prices of the security.
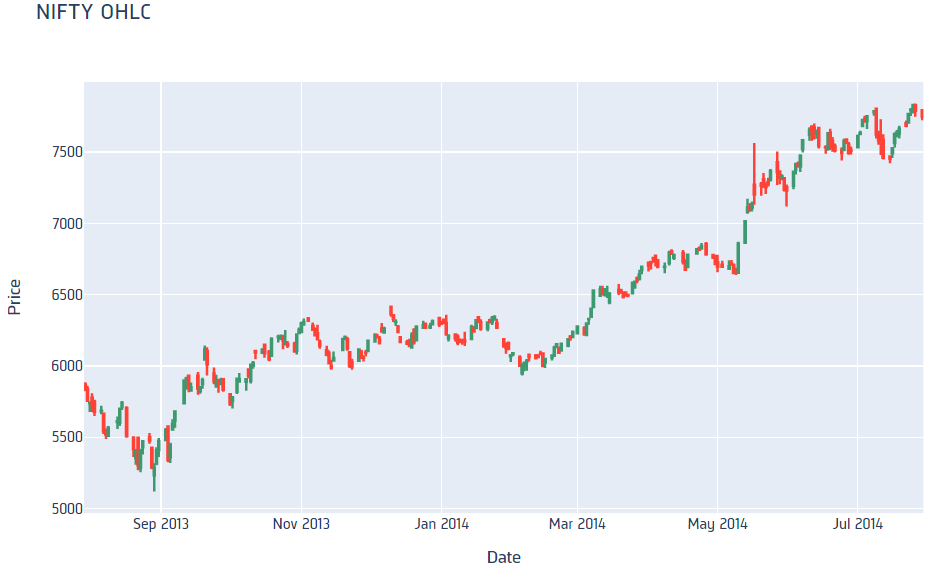
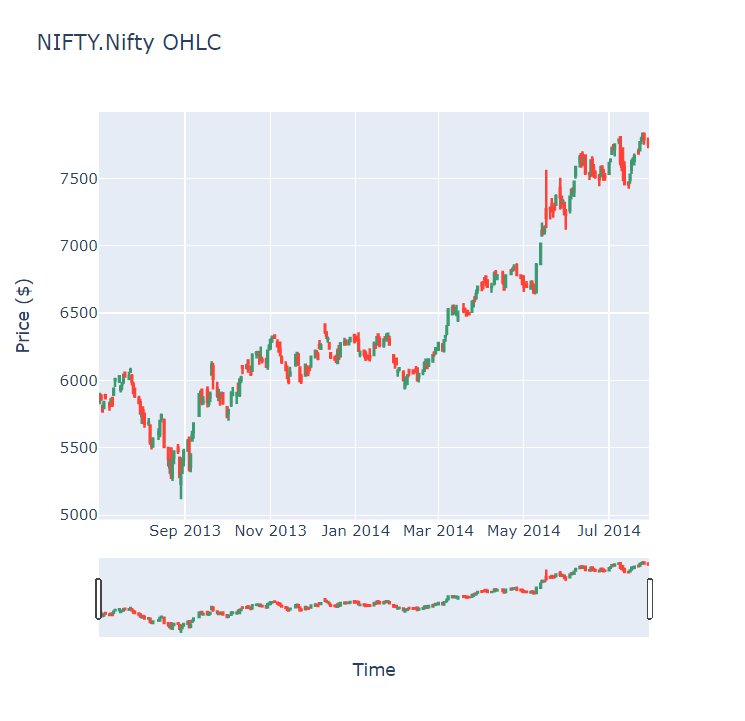
Line Chart
Follow these steps to plot line charts using built-in methodsPlotly.NET package:
- Select data to plot.
- Call the
plotmethod on thepandasobject. - Create a
Linechart. - Create a
Layout. - Assign the
Layoutto the chart. - Show the plot.
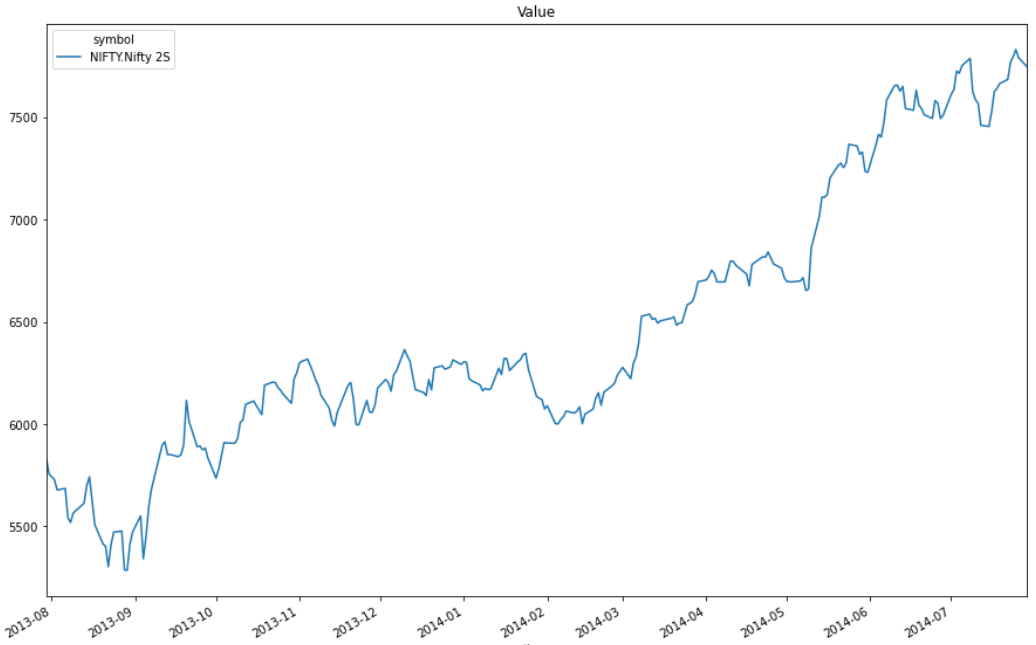
values = history['value'].unstack(level=0)
values.plot(title="Value", figsize=(15, 10))
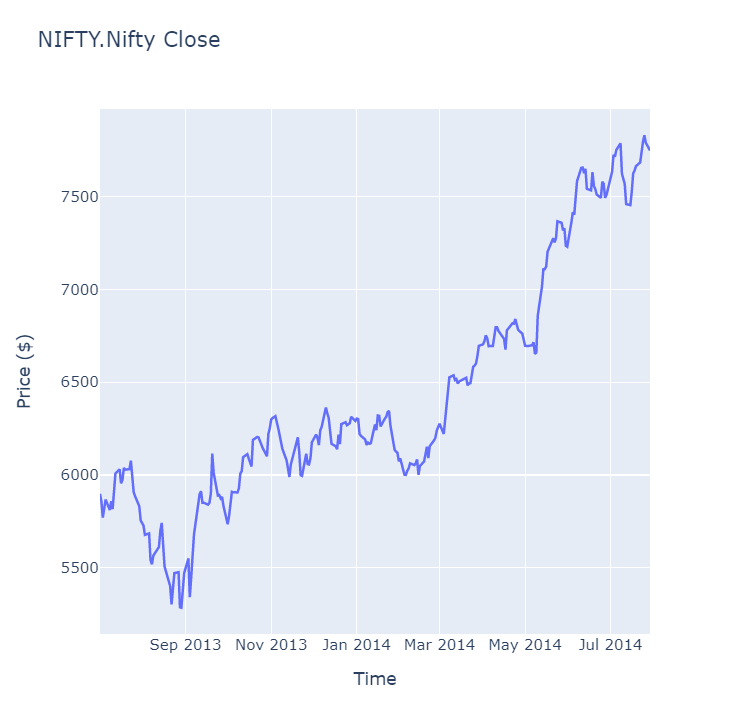
var chart = Chart2D.Chart.Line<DateTime, decimal, string>(
history.Select(x => x.EndTime),
history.Select(x => x.Close)
);
LinearAxis xAxis = new LinearAxis();
xAxis.SetValue("title", "Time");
LinearAxis yAxis = new LinearAxis();
yAxis.SetValue("title", "Price ($)");
Title title = Title.init($"{symbol} Close");
Layout layout = new Layout();
layout.SetValue("xaxis", xAxis);
layout.SetValue("yaxis", yAxis);
layout.SetValue("title", title);
chart.WithLayout(layout);
plt.show()
HTML(GenericChart.toChartHTML(chart))
Line charts display the value of the property you selected in a time series.