Popular Libraries
Tensorflow
Create Subscriptions
In the Initializeinitialize method, subscribe to some data so you can train the tensorflow model and make predictions.
# Add a security and save a reference to its Symbol.
self._symbol = self.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol
Build Models
In this example, build a neural-network regression prediction model that uses the following features and labels:
| Data Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Features | The last 5 close price differencing compared to current price |
| Labels | The following day's price change |
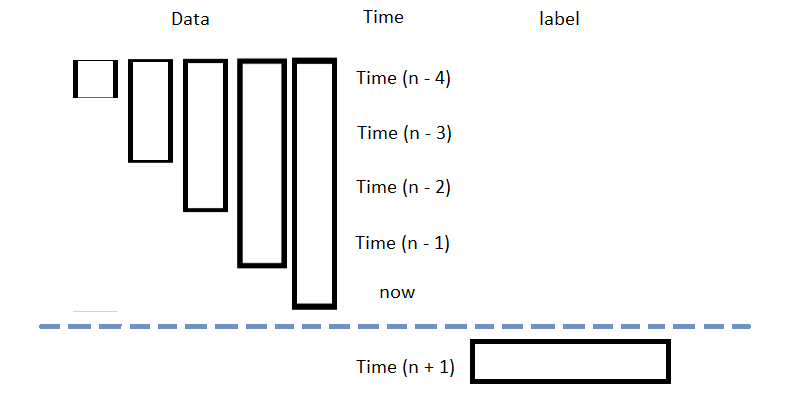
The following image shows the time difference between the features and labels:
Follow these steps to create a method to build the model:
- Define some parameters, including the number of factors, neurons, and epochs.
- Create the model using built-in Keras API.
# Set some hyperparameters: num_factors = 5 # Set the number of input features. num_neurons_1 = 10 # Set the neurons in each hidden layer to capture complexity. num_neurons_2 = 10 num_neurons_3 = 5 self.epochs = 20 # Set the training epochs for sufficient learning. self.learning_rate = 0.0001 # Set the learning rate for optimization control.
# Define the model with sequential layers: an input layer with ReLU activation to introduce non-linearity,
# two hidden layers for feature extraction, and an output layer for predictions.
self.model = tf.keras.sequential([
tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_1, activation=tf.nn.relu, input_shape=(num_factors,)), # The input shape is required.
tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_2, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_3, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.dense(1)
])
Train Models
You can train the model at the beginning of your algorithm and you can periodically re-train it as the algorithm executes.
Warm Up Training Data
You need historical data to initially train the model at the start of your algorithm. To get the initial training data, in the Initializeinitialize method, make a history request.
# Fill a RollingWindow with 300 days of historical closing prices.
training_length = 300
self.training_data = RollingWindow(training_length)
history = self.history[TradeBar](self._symbol, training_length, Resolution.DAILY)
for trade_bar in history:
self.training_data.add(trade_bar.close)
Define a Training Method
To train the model, define a method that fits the model with the training data.
# Prepare feature and label data for training by processing the RollingWindow data into a time series.
def get_features_and_labels(self, lookback=5):
lookback_series = []
data = pd.Series(list(self.training_data)[::-1])
for i in range(1, lookback + 1):
df = data.diff(i)[lookback:-1]
df.name = f"close-{i}"
lookback_series.append(df)
X = pd.concat(lookback_series, axis=1).reset_index(drop=True).dropna()
Y = data.diff(-1)[lookback:-1].reset_index(drop=True)
return X.values, Y.values
def my_training_method(self):
features, labels = self.get_features_and_labels()
# Define the loss function. We use MSE in this example.
def loss_mse(target_y, predicted_y):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(target_y - predicted_y))
# Train the model.
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.adam(learning_rate=self.learning_rate)
for i in range(self.epochs):
with tf.gradient_tape() as t:
loss = loss_mse(labels, self.model(features))
jac = t.gradient(loss, self.model.trainable_weights)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(jac, self.model.trainable_weights))
Set Training Schedule
To train the model at the beginning of your algorithm, in the Initializeinitialize method, call the Traintrain method.
# Train the model initially to provide a baseline for prediction and decision-making. self.train(self.my_training_method)
To periodically re-train the model as your algorithm executes, in the Initializeinitialize method, schedule some training sessions.
# Train the model every Sunday at 8:00 AM self.train(self.date_rules.every(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY), self.time_rules.at(8, 0), self.my_training_method)
Update Training Data
To update the training data as the algorithm executes, in the OnDataon_data method, add the current close price to the RollingWindow that holds the training data.
# Add the latest closing price to the training data to ensure the model is trained with the most recent market data.
def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
if self._symbol in slice.bars:
self.training_data.add(slice.bars[self._symbol].close)
Predict Labels
To predict the labels of new data, in the OnDataon_data method, get the most recent set of features and then call the run method with new features.
# Get the current feature set and make a prediction. new_features, __ = self.get_features_and_labels() prediction = self.model(new_features) prediction = float(prediction.numpy()[-1])
You can use the label prediction to place orders.
# Place orders based on the forecasted market direction.
if prediction > 0:
self.SetHoldings(self._symbol, 1)
elif prediction < 0:
self.SetHoldings(self._symbol, -1)
Save Models
Follow these steps to save Tensorflow models into the Object Store:
- Set the key name of the model to be stored in the Object Store.
- Call the
GetFilePathget_file_pathmethod with the key. - Call the
savemethod with the model and file path. - Save the model to the file path.
# Set the key to store the model in the Object Store so you can use it later. model_key = "model.keras"
Note that the model has to have the suffix .keras.
# Get the file path to correctly save and access the model in Object Store. file_name = self.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
This method returns the file path where the model will be stored.
# Serialize the model and save it to the file. model.save(file_name)
# Save the model to object store to capture model state for reusability. self.object_store.save(model_key)
Load Models
You can load and trade with pre-trained tensorflow models that you saved in the Object Store. To load a tensorflow model from the Object Store, in the Initializeinitialize method, get the file path to the saved model and then recall the graph and weights of the model.
# Load the tensorflow model from the Object Store to use its saved state and update it with new data if needed.
def initialize(self) -> None:
model_key = 'model.keras'
if self.object_store.contains_key(model_key):
file_name = self.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
self.model = tf.keras.models.load_model(file_name)
The ContainsKeycontains_key method returns a boolean that represents if the model.keras is in the Object Store. If the Object Store doesn't contain the keys, save the model using them before you proceed.
Examples
The following examples demonstrate some common practices for using
Keras
library.
Example 1: Multi-layer Perceptron Model
The below algorithm makes use of
Keras
library to predict the future price movement using the previous 5 OHLCV data. The model is built with multi-layer perceptrons, ReLu activation function, and Adam optimization. It is trained using rolling 2-year data. To ensure the model applicable to the current market environment, we recalibrate the model on every Sunday.
import tensorflow as tf
class TensorFlowAlgorithm(QCAlgorithm):
def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
self.set_cash(100000)
# Request SPY data for model training, prediction and trading.
self.symbol = self.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol
# Hyperparameter to create the MLP model.
num_factors = 5
num_neurons_1 = 10
num_neurons_2 = 10
num_neurons_3 = 5
self.epochs = 100
self.learning_rate = 0.0001
# Create the MLP model with ReLu activiation.
self.model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_neurons_1, activation=tf.nn.relu, input_shape=(num_factors,)), # input shape required
tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_neurons_2, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_neurons_3, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
# 2-year data to train the model.
training_length = 500
self.training_data = RollingWindow(training_length)
# Warm up the training dataset to train the model immediately.
history = self.history[TradeBar](self.symbol, training_length, Resolution.DAILY)
for trade_bar in history:
self.training_data.add(trade_bar.close)
# Train the model to use the prediction right away.
self.train(self.my_training_method)
# Recalibrate the model weekly to ensure its accuracy on the updated domain.
self.train(self.date_rules.week_start(), self.time_rules.at(8, 0), self.my_training_method)
def get_features_and_labels(self, lookback=5) -> None:
lookback_series = []
# Train and predict the N differencing data, which is more normalized and stationary.
data = pd.Series(list(self.training_data)[::-1])
for i in range(1, lookback + 1):
df = data.diff(i)[lookback:-1]
df.name = f"close-{i}"
lookback_series.append(df)
X = pd.concat(lookback_series, axis=1).reset_index(drop=True).dropna()
Y = data.diff(-1)[lookback:-1].reset_index(drop=True)
return X.values, Y.values
def my_training_method(self) -> None:
# Prepare the processed training data.
features, labels = self.get_features_and_labels()
# Define the loss function, we use MSE in this example
def loss_mse(target_y, predicted_y):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(target_y - predicted_y))
# Train the model with Adam optimization function.
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=self.learning_rate)
for i in range(self.epochs):
with tf.GradientTape() as t:
loss = loss_mse(labels, self.model(features))
jac = t.gradient(loss, self.model.trainable_weights)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(jac, self.model.trainable_weights))
def on_data(self, data) -> None:
if data.bars.contains_key(self.symbol):
self.training_data.add(data.bars[self.symbol].close)
# Get prediction by the updated features.
new_features, __ = self.get_features_and_labels()
prediction = self.model(new_features)
prediction = float(prediction.numpy()[-1])
# If the predicted direction is going upward, buy SPY, else sell.
self.set_holdings(self.symbol, 1 if prediction > 0 else -1)