Option Strategies
Short Call Butterfly
Introduction
The short call butterfly strategy is the combination of a bull call spread and a bear call spread. In the call butterfly, all of the calls should have the same underlying Equity, the same expiration date, and the same strike price distance between the ITM-ATM and OTM-ATM call pairs. The short call butterfly consists of a short ITM call, a short OTM call, and 2 long ATM calls. This strategy profits from high volatility in the underlying Equity price.
Implementation
Follow these steps to implement the short call butterfly strategy:
- In the
Initializeinitializemethod, set the start date, end date, cash, and Option universe. - In the
OnDataon_datamethod, select the contracts of the strategy legs. - In the
OnDataon_datamethod, place the orders.
private Symbol _symbol;
public override void Initialize()
{
SetStartDate(2024, 9, 1);
SetEndDate(2024, 12, 31);
SetCash(500000);
UniverseSettings.Asynchronous = true;
var option = AddOption("GOOG", Resolution.Minute);
_symbol = option.Symbol;
option.SetFilter(universe => universe.CallButterfly(30, 5));
} def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
self.set_cash(500000)
self.universe_settings.asynchronous = True
option = self.add_option("GOOG", Resolution.MINUTE)
self._symbol = option.symbol
option.set_filter(lambda universe: universe.call_butterfly(30, 5))
The CallButterflycall_butterfly filter narrows the universe down to just the three contracts you need to form a short call butterfly.
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
if (Portfolio.Invested ||
!slice.OptionChains.TryGetValue(_symbol, out var chain))
{
return;
}
// Select the call Option contracts with the furthest expiry
var expiry = chain.Max(x =x> x.Expiry);
var calls = chain.Where(x => x.Expiry == expiry && x.Right == OptionRight.Call);
if (calls.Count() == 0) return;
// Select the ATM, ITM and OTM contracts from the remaining contracts
var atmCall = calls.OrderBy(x => Math.Abs(x.Strike - chain.Underlying.Price)).First();
var itmCall = calls.OrderBy(x => x.Strike).Skip(1).First();
var otmCall = calls.Single(x => x.Strike == atmCall.Strike * 2 - itmCall.Strike); def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
if self.portfolio.invested:
return
# Get the OptionChain
chain = slice.option_chains.get(self._symbol, None)
if not chain:
return
# Get the furthest expiry date of the contracts
expiry = max([x.expiry for x in chain])
# Select the call Option contracts with the furthest expiry
calls = [i for i in chain if i.expiry == expiry and i.right == OptionRight.CALL]
if len(calls) == 0:
return
# Select the ATM, ITM and OTM contracts from the remaining contracts
atm_call = sorted(calls, key=lambda x: abs(x.strike - chain.underlying.price))[0]
itm_call = sorted(calls, key=lambda x: x.strike)[1]
otm_call = [x for x in calls if x.strike == atm_call.strike * 2 - itm_call.strike][0]
Approach A: Call the OptionStrategies.ShortButterflyCallOptionStrategies.short_butterfly_call method with the details of each leg and then pass the result to the Buybuy method.
var optionStrategy = OptionStrategies.ShortButterflyCall(_symbol, otmCall.Strike, atmCall.Strike, itmCall.Strike, expiry); Buy(optionStrategy, 1);
option_strategy = OptionStrategies.short_butterfly_call(self._symbol, otm_call.strike, atm_call.strike, itm_call.strike, expiry) self.buy(option_strategy, 1)
Approach B: Create a list of Leg objects and then call the Combo Market Ordercombo_market_order, Combo Limit Ordercombo_limit_order, or Combo Leg Limit Ordercombo_leg_limit_order method.
var legs = new List<Leg>()
{
Leg.Create(atmCall.Symbol, 2),
Leg.Create(itmCall.Symbol, -1),
Leg.Create(otmCall.Symbol, -1)
};
ComboMarketOrder(legs, 1); legs = [
Leg.create(atm_call.symbol, 2),
Leg.create(itm_call.symbol, -1),
Leg.create(otm_call.symbol, -1)
]
self.combo_market_order(legs, 1)
If the Option is American Option, there is a risk of early assignment on the contracts you sell.
Strategy Payoff
The short call butterfly is a limited-reward-limited-risk strategy. The payoff is
$$ \begin{array}{rcll} C^{OTM}_T & = & (S_T - K^{OTM})^{+}\\ C^{ITM}_T & = & (S_T - K^{ITM})^{+}\\ C^{ATM}_T & = & (S_T - K^{ATM})^{+}\\ P_T & = & (2\times C^{ATM}_T - C^{OTM}_T - C^{ITM}_T - 2\times C^{ATM}_0 + C^{ITM}_0 + C^{OTM}_0)\times m - fee \end{array} $$ $$ \begin{array}{rcll} \textrm{where} & C^{OTM}_T & = & \textrm{OTM call value at time T}\\ & C^{ITM}_T & = & \textrm{ITM call value at time T}\\ & C^{ATM}_T & = & \textrm{ATM call value at time T}\\ & S_T & = & \textrm{Underlying asset price at time T}\\ & K^{OTM} & = & \textrm{OTM call strike price}\\ & K^{ITM} & = & \textrm{ITM call strike price}\\ & K^{ATM} & = & \textrm{ATM call strike price}\\ & P_T & = & \textrm{Payout total at time T}\\ & C^{ITM}_0 & = & \textrm{ITM call value at position opening (credit received)}\\ & C^{OTM}_0 & = & \textrm{OTM call value at position opening (credit received)}\\ & C^{ATM}_0 & = & \textrm{ATM call value at position opening (debit paid)}\\ & m & = & \textrm{Contract multiplier}\\ & T & = & \textrm{Time of expiration} \end{array} $$The following chart shows the payoff at expiration:
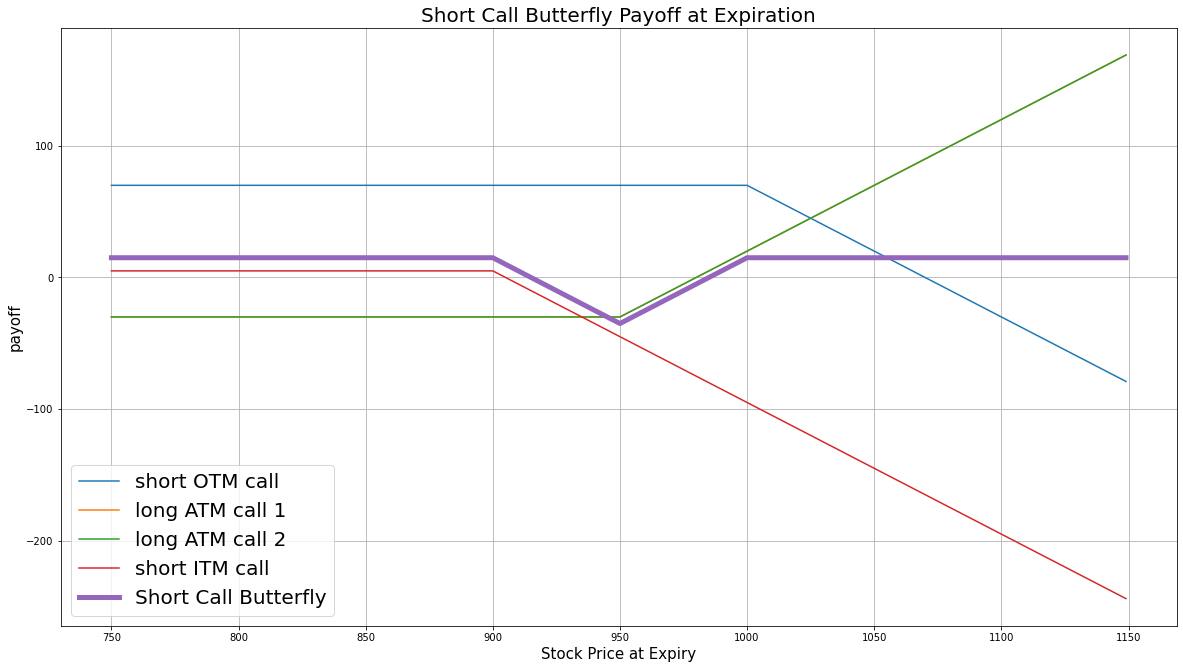
The maximum profit is the net credit received: $C^{ITM}_0 + C^{OTM}_0 - 2\times C^{ATM}_0$. It occurs when the underlying price is less than ITM strike or greater than OTM strike at expiration.
The maximum loss is $K^{ATM} - K^{ITM} + C^{ITM}_0 + C^{OTM}_0 - 2\times C^{ATM}_0$. It occurs when the underlying price is at the same level as when you opened the trade.
If the Option is American Option, there is a risk of early assignment on the contracts you sell.
Example
The following table shows the price details of the assets in the short call butterfly:
| Asset | Price ($) | Strike ($) |
|---|---|---|
| OTM call | 4.90 | 767.50 |
| ATM call | 15.00 | 800.00 |
| ITM call | 41.00 | 832.50 |
| Underlying Equity at expiration | 829.08 | - |
Therefore, the payoff is
$$ \begin{array}{rcll} C^{OTM}_T & = & (S_T - K^{OTM})^{+}\\ & = & (767.50-829.08)^{+}\\ & = & 0\\ C^{ITM}_T & = & (S_T - K^{ITM})^{+}\\ & = & (832.50-829.08)^{+}\\ & = & 3.42\\ C^{ATM}_T & = & (S_T - K^{ATM})^{+}\\ & = & (800.00-829.08)^{+}\\ & = & 0\\ P_T & = & (-C^{OTM}_T - C^{ITM}_T + 2\times C^{ATM}_T - 2\times C^{ATM}_0 + C^{ITM}_0 + C^{OTM}_0)\times m - fee\\ & = & (-0-3.42+0\times2+4.90+41.00-15.00\times2)\times100-1.00\times4\\ & = & -1252 \end{array} $$So, the strategy gains $1,244.
The following algorithm implements a short call butterfly Option strategy:
public class BearPutSpreadStrategy : QCAlgorithm
{
private Symbol _symbol;
public override void Initialize()
{
SetStartDate(2024, 9, 1);
SetEndDate(2024, 12, 31);
SetCash(500000);
var option = AddOption("GOOG", Resolution.Minute);
_symbol = option.Symbol;
option.SetFilter(universe => universe.CallButterfly(30, 5));
}
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
if (Portfolio.Invested) return;
// Get the OptionChain of the symbol
var chain = slice.OptionChains.get(_symbol, null);
if (chain == null || chain.Count() == 0) return;
// sorted the optionchain by expiration date and choose the furthest date
var expiry = chain.OrderByDescending(x => x.Expiry).First().Expiry;
// filter the call options from the contracts which expire on the furthest expiration date in the option chain.
var calls = chain.Where(x => x.Expiry == expiry && x.Right == OptionRight.Call);
if (calls.Count() == 0) return;
// sort the call options with the same expiration date according to their strike price.
var callStrikes = calls.Select(x => x.Strike).OrderBy(x => x);
// get at-the-money strike
var atmStrike = calls.OrderBy(x => Math.Abs(x.Strike - chain.Underlying.Price)).First().Strike;
// Get the distance between lowest strike price and ATM strike, and highest strike price and ATM strike.
// Get the lower value as the spread distance as equidistance is needed for both side.
var spread = Math.Min(Math.Abs(callStrikes.First() - atmStrike), Math.Abs(callStrikes.Last() - atmStrike));
// select the strike prices for forming the option legs
var itmStrike = atmStrike - spread;
var otmStrike = atmStrike + spread;
var optionStrategy = OptionStrategies.ShortButterflyCall(_symbol, otmStrike, atmStrike, itmStrike, expiry);
// We open a position with 1 unit of the option strategy
Buy(optionStrategy, 1);
}
} class LongCallButterflyStrategy(QCAlgorithm):
def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
self.set_cash(500000)
option = self.add_option("GOOG", Resolution.MINUTE)
self.symbol = option.symbol
option.set_filter(self.universe_func)
def universe_func(self, universe: OptionFilterUniverse) -> OptionFilterUniverse:
return universe.call_butterfly(30, 5)
def on_data(self, data: Slice) -> None:
# avoid extra orders
if self.portfolio.invested: return
# Get the OptionChain of the self.symbol
chain = data.option_chains.get(self.symbol, None)
if not chain: return
# sorted the optionchain by expiration date and choose the furthest date
expiry = sorted(chain, key = lambda x: x.expiry, reverse=True)[0].expiry
# filter the call options from the contracts which expire on the furthest expiration date in the option chain.
calls = [i for i in chain if i.expiry == expiry and i.right == OptionRight.CALL]
if len(calls) == 0: return
# sort the call options with the same expiration date according to their strike price.
call_strikes = sorted([x.strike for x in calls])
# get at-the-money strike
atm_strike = sorted(calls, key=lambda x: abs(x.strike - chain.underlying.price))[0].strike
# Get the distance between lowest strike price and ATM strike, and highest strike price and ATM strike.
# Get the lower value as the spread distance as equidistance is needed for both side.
spread = min(abs(call_strikes[0] - atm_strike), abs(call_strikes[-1] - atm_strike))
# select the strike prices for forming the option legs
itm_strike = atm_strike - spread
otm_strike = atm_strike + spread
option_strategy = OptionStrategies.short_butterfly_call(self.symbol, otm_strike, atm_strike, itm_strike, expiry)
# We open a position with 1 unit of the option strategy
self.buy(option_strategy, 1)
Other Examples
For more examples, see the following algorithms: