Popular Libraries
Aesera
Introduction
This page explains how to build, train, deploy and store Aesera models.
Create Subscriptions
In the Initializeinitialize method, subscribe to some data so you can train the sklearn model and make predictions.
# Add a security and save a reference to its Symbol.
self._symbol = self.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol
Build Models
In this example, build a logistic regression prediction model that uses the following features and labels:
| Data Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Features | Normalized daily close price of the SPY over the last 5 days |
| Labels | Return direction of the SPY over the next day |
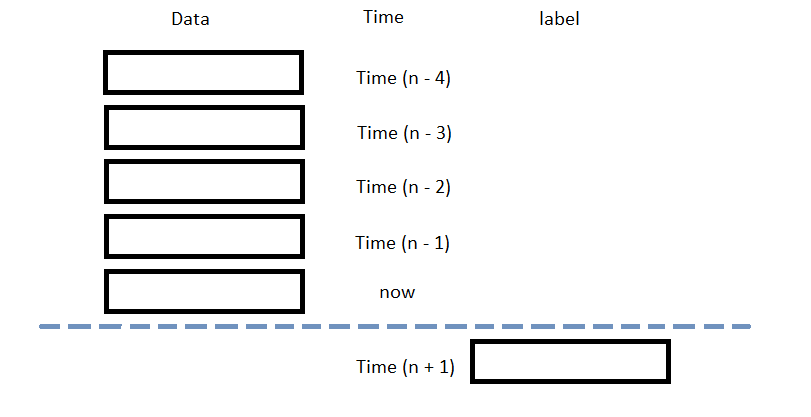
The following image shows the time difference between the features and labels:
Follow the below steps to build the model:
- Initialize variables.
- Construct the model graph.
- Compile the model.
# Declare Aesara's symbolic variables.
x = at.dmatrix("x")
y = at.dvector("y")
# Initialize a NumPy random number generator with a fixed seed for reproducibility.
rng = np.random.default_rng(100)
# Initialize the weight vector w randomly using shared so the model coefficients keep their values
# between training iterations (updates).
w = aesara.shared(rng.standard_normal(5), name="w")
# Initialize the bias term.
b = aesara.shared(0., name="b")
# Construct the Aesara expression graph. p_1 = 1 / (1 + at.exp(-at.dot(x, w) - b)) # Logistic transformation. prediction = p_1 > 0.5 # The prediction thresholded. xent = y * at.log(p_1) - (1 - y) * at.log(1 - p_1) # Cross-entropy log-loss function. cost = xent.mean() + 0.01 * (w ** 2).sum() # The cost to minimize (MSE). gw, gb = at.grad(cost, [w, b]) # Compute the gradient of the cost.
# Define training and prediction functions with Aesara to optimize weights
# and biases during training and generate predictions.
self.train = aesara.function(
inputs=[x, y],
outputs=[prediction, xent],
# Update weights and biases.
updates=((w, w - 0.1 * gw), (b, b - 0.1 * gb)))
self.predict = aesara.function(inputs=[x], outputs=prediction)
Train Models
You can train the model at the beginning of your algorithm and you can periodically re-train it as the algorithm executes.
Warm Up Training Data
You need historical data to initially train the model at the start of your algorithm. To get the initial training data, in the Initializeinitialize method, make a history request.
# Fill a RollingWindow with 2 years of training data.
training_length = 252*2
self.training_data = RollingWindow(training_length)
history = self.history[TradeBar](self._symbol, training_length, Resolution.DAILY)
for trade_bar in history:
self.training_data.add(trade_bar)
Define a Training Method
To train the model, define a method that fits the model with the training data.
# Prepare feature and label data for training.
def get_features_and_labels(self, n_steps=5):
training_df = self.PandasConverter.GetDataFrame[TradeBar](list(self.training_data)[::-1])['close']
features = []
for i in range(1, n_steps + 1):
close = training_df.shift(i)[n_steps:-1]
close.name = f"close-{i}"
features.append(close)
features = pd.concat(features, axis=1)
# Normalize using the 5 day interval.
features = MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(features.T).T[4:]
Y = training_df.pct_change().shift(-1)[n_steps*2-1:-1].reset_index(drop=True)
labels = np.array([1 if y > 0 else 0 for y in Y]) # Binary class.
return features, labels
def my_training_method(self):
features, labels = self.get_features_and_labels()
D = (features, labels)
self.train(D[0], D[1])
Set Training Schedule
To train the model at the beginning of your algorithm, in the Initializeinitialize method, call the Traintrain method.
# Train the model right now. self.train(self.my_training_method)
To periodically re-train the model as your algorithm executes, in the Initializeinitialize method, call the Traintrain method as a Scheduled Event.
# Train the model every Sunday at 8:00 AM. self.train(self.date_rules.every(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY), self.time_rules.at(8, 0), self.my_training_method)
Update Training Data
To update the training data as the algorithm executes, in the OnDataon_data method, add the current TradeBar to the RollingWindow that holds the training data.
# Add the current bar to the training data to ensure the model trains with the most recent market data.
def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
if self._symbol in slice.bars:
self.training_data.add(slice.bars[self._symbol])
Predict Labels
To predict the labels of new data, in the OnDataon_data method, get the most recent set of features and then call the predict method.
# Get the feature set and make a prediction. features, _ = self.get_features_and_labels() prediction = self.predict(features[-1].reshape(1, -1)) prediction = float(prediction)
You can use the label prediction to place orders.
# Place orders based on the prediction.
if prediction == 1:
self.set_holdings(self._symbol, 1)
elif prediction == 0:
self.set_holdings(self._symbol, -1)
Save Models
Follow these steps to save sklearn models into the Object Store:
- Set the key name you want to store the model under in the Object Store.
- Call the
GetFilePathget_file_pathmethod with the key. - Call the
dumpmethod the file path.
# Set the storage key to something representative. model_key = "model"
# Get the file path to save and access the model in the Object Store. file_name = self.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
This method returns the file path where the model will be stored.
# Serialize and save the model. joblib.dump(self.predict, file_name)
If you dump the model using the joblib module before you save the model, you don't need to retrain the model.
Load Models
You can load and trade with pre-trained sklearn models that you saved in the Object Store. To load a sklearn model from the Object Store, in the Initializeinitialize method, get the file path to the saved model and then call the load method.
# Load the trained Aesera model from the Object Store.
def initialize(self) -> None:
if self.object_store.contains_key(model_key):
file_name = self.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
self.model = joblib.load(file_name)
The ContainsKeycontains_key method returns a boolean that represents if the model_key is in the Object Store. If the Object Store does not contain the model_key, save the model using the model_key before you proceed.
Examples
The following examples demonstrate some common practices for using
Aesera
library.
Example 1: Aesera
The below algorithm makes use of
Aesera
library to predict the future price movement using the previous 5 OHLCV data. The model is trained using rolling 2-year data. To ensure the model applicable to the current market environment, we recalibrate the model on every Sunday.
import aesara
import aesara.tensor as at
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import joblib
class AeseraExampleAlgorithm(QCAlgorithm):
def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
self.set_cash(100000)
# Request SPY data for model training, prediction and trading.
self.symbol = self.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol
# 2-year data to train the model.
training_length = 252*2
self.training_data = RollingWindow(training_length)
# Warm up the training dataset to train the model immediately.
history = self.history[TradeBar](self.symbol, training_length, Resolution.DAILY)
for trade_bar in history:
self.training_data.add(trade_bar)
# Retrieve already trained model from object store to use immediately.
#if self.object_store.contains_key("train") and self.object_store.contains_key("predict"):
# train_file_name = self.object_store.get_file_path("train")
# predict_file_name = self.object_store.get_file_path("predict")
# self.predict = joblib.load(train_file_name)
# self.predict = joblib.load(predict_file_name)
#else:
# Declare Aesara symbolic variables.
x = at.dmatrix("x")
y = at.dvector("y")
# initialize the weight vector w randomly.
# this and the following bias variable b
# are shared so they keep their values
# between training iterations (updates)
rng = np.random.default_rng(100)
w = aesara.shared(rng.standard_normal(5), name="w")
# initialize the bias term.
b = aesara.shared(0., name="b")
# Construct Aesara expression graph.
p_1 = 1 / (1 + at.exp(-at.dot(x, w) - b)) # Probability that target = 1
prediction = p_1 > 0.5 # The prediction thresholded
xent = y * at.log(p_1) - (1-y) * at.log(1-p_1) # Cross-entropy log-loss function
cost = xent.mean() + 0.01 * (w ** 2).sum() # The cost to minimize
gw, gb = at.grad(cost, [w, b]) # Compute the gradient of the cost
# w.r.t weight vector w and
# bias term b (we shall
# return to this in a
# following section of this
# tutorial)
# Compile the model and train it later.
self._train = aesara.function(
inputs=[x, y],
outputs=[prediction, xent],
updates=((w, w - 0.1 * gw), (b, b - 0.1 * gb)))
self.predict = aesara.function(inputs=[x], outputs=prediction)
# Train the model to use the prediction right away.
self.train(self.my_training_method)
# Recalibrate the model weekly to ensure its accuracy on the updated domain.
self.train(self.date_rules.every(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY), self.time_rules.at(8,0), self.my_training_method)
def get_features_and_labels(self, n_steps=5) -> None:
# Train and predict the return data, which is more normalized and stationary.
training_df = self.pandas_converter.get_data_frame[TradeBar](list(self.training_data)[::-1])['close']
# Stack the data for 5-day OHLCV data per each sample to train with.
features = []
for i in range(1, n_steps + 1):
close = training_df.shift(i)[n_steps:-1]
close.name = f"close-{i}"
features.append(close)
features = pd.concat(features, axis=1)
# Normalize using the 5 day interval.
features = MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(features.T).T[4:]
Y = training_df.pct_change().shift(-1)[n_steps*2-1:-1].reset_index(drop=True)
# Train to predict the direction only.
labels = np.array([1 if y > 0 else 0 for y in Y]) # binary class
return features, labels
def my_training_method(self) -> None:
# Prepare the processed training data.
features, labels = self.get_features_and_labels()
D = (features, labels)
# Recalibrate the model based on updated data.
self._train(D[0], D[1])
# Store the model to object store to retrieve it in other instances in case the algorithm stops.
model_key = "model_test_aesera"
file_name = self.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
joblib.dump(self.predict, file_name)
self.object_store.save(model_key)
def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
if self.symbol in slice.bars:
self.training_data.add(slice.bars[self.symbol])
# Get prediction using the latest 5 OHLCV.
features, _ = self.get_features_and_labels()
prediction = self.predict(features[-1].reshape(1, -1))
prediction = float(prediction)
# If the predicted direction is going upward, buy SPY.
if prediction == 1:
self.set_holdings(self.symbol, 1)
# If the predicted direction is going downward, sell SPY.
elif prediction == 0:
self.set_holdings(self.symbol, -1)

