Slippage
Supported Models
Introduction
This page describes the pre-built slippage models in LEAN. If none of these models perform exactly how you want, create a custom slippage model.
Null Model
The NullSlippageModel sets the slippage of each order to zero. It's the default slippage model of the DefaultBrokerageModel.
security.SetSlippageModel(NullSlippageModel.Instance);
security.set_slippage_model(NullSlippageModel.INSTANCE)
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.
Constant Model
The ConstantSlippageModel applies a constant percentage of slippage to each order.
security.SetSlippageModel(new ConstantSlippageModel(0.01m));
security.set_slippage_model(ConstantSlippageModel(0.01))
The following table describes the arguments the model accepts:
| Argument | Data Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
slippagePercentslippage_percent | decimalfloat | The slippage percent for each order. The value must be in the interval (0, 1). |
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.
Volume Share Model
The VolumeShareSlippageModel calculates the slippage of each order by multiplying the price impact constant by the square of the ratio of the order to the total volume. If the volume of the current bar is zero, the slippage percent is
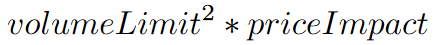
where volumeLimit and priceImpact are custom input variables. If the volume of the current bar is positive, the slippage percent is
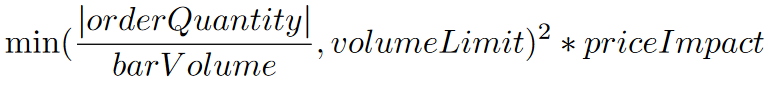
where orderQuantity is the quantity of the order and barVolume is the volume of the current bar. If the security subscription provides TradeBar data, the barVolume is the volume of the current bar. If the security subscription provides QuoteBar data, the barVolume is the bid or ask size of the current bar. CFD, Forex, and Crypto data often doesn't include volume. If there is no volume reported for these asset classes, the model returns zero slippage.
security.SetSlippageModel(new VolumeShareSlippageModel());
security.set_slippage_model(VolumeShareSlippageModel())
The following table describes the arguments the model accepts:
| Argument | Data Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
volumeLimitvolume_limit | decimalfloat | Maximum percent of historical volume that can fill in each bar. 0.5 means 50% of historical volume. 1.0 means 100%. | 0.025 |
priceImpactprice_impact | decimalfloat | Scaling coefficient for price impact. Larger values will result in more simulated price impact. Smaller values will result in less simulated price impact. | 0.1 |
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.
Market Impact Model
The MarketImpactSlippageModel calculates the slippage with perspective to the market impact created by an order, which mimics the consumption of the order book and disruption of the supply-demand relationship at the microeconomic scale.
The model is divided into distinct parts, the market impact estimation and the slippage that results from it.
Factors to Consider
The model includes factors that create market impact. Almgren, Thum, Hauptmann & Li (2005) suggested the following factors:
- Execution Time
- Volatility of the Underlying Securities
- Liquidity
- Order Size
Asset price time series is usually considered as Random walk (with/without drift) $$S_t = S_{t-1} + f(S, t) + \epsilon$$ or Brownian Motion $$S_t = S_0 + exp((\mu-\frac{1}{2}\sigma^2)t + \sigma W_t)$$ In either model, the variance of predictions increases over time ($Var(S)=\sigma\sqrt{t}$). In fact, this happens to most stock price models. Thus, time uncertainty should also apply to the concept of slippage. The longer it takes to go from order submission to execution, the further the fill price will be from the price at order submission.
Like (1), the volatility also contributes to the uncertainty of the next price ($Var(S)=\sigma\sqrt{t}$). In most cases, volatility has a one-sided impact since the market's volatility is often introduced by overbuying or overselling from positive or negative sentiments.
Liquidity plays a crucial role in the supply-demand resilience. When a stock is liquid, an order usually only takes a small fraction of the market depth. Hence, the gap between the bid and ask price can be refilled quickly due to high market participation and a small gap. However, when a stock is illiquid, a single order might already take the top few layers of the order book, creating a wide gap between the bid and ask price and volume, which makes a bigger shift in the equilibrium price. This will create an impact which is permanent in nature.

Last but not least, the order size directly affects the proportion of the order book/liquidity that the order consumes. Moreover, the larger the order is, the longer it takes to fill since the market might not have sufficient depth. This has interaction effects with the preceding factors.
Market Impact Decomposition
In the book "A Signal Processing Perspective on Financial Engineering", Feng & Palomer (2015) generalized scholars' opinions that market impact can be broken down into "permanent" and "temporary" components, with noise. The permanent impact of a trade refers to the price differences between equilibrium prices before and after the trade and the resilience of the order book. In contrast, temporary impact refers to the price difference between the instant price drop after a trade and the post-trade equilibrium.

The model incorporates the preceding factors and estimates both the permanent and temporary impact components with two diffusion models as a function of $\nu=\frac{X}{VT}$, which is the normalized order size: $$G\left(\nu\right)=\pm\gamma\left|\nu\right|^\alpha+\text{noise}$$ $$H\left(\nu\right)=\pm\eta\left|\nu\right|^\beta+\text{noise}$$ where $X$ is the order quantity, $V$ is the average daily volume, and $T$ is the time difference between order submission and filling (execution time). The other symbols are parameters that are calibrated from historical trade data. Together with the execution time, daily volatility $\sigma$, and liquidity factor $\delta$, the complete models are as follows: $$I=\sigma T \gamma\left|\frac{X}{VT}\right|^\alpha\left(\frac{\Theta}{V}\right)^\delta+\sigma\sqrt{T_{\text{post}}}\epsilon$$ $$J=\sigma T \eta\left|\frac{X}{VT}\right|^\beta+\sigma\sqrt{T_{\text{post}}}\epsilon$$ where $\Theta$ is the share outstanding, $T_{post}$ is the time difference between order submission and the new equilibrium established, $I$ is the permanent market impact, and $J$ is the temporary market impact. The inverse of the turnover rate $\frac{\Theta}{V}$ contributes to the permanent impact. This relationship is reasonable since higher turnover means more market participants are in the market, so the order book depth is deeper.
Implementation
security.SetSlippageModel(new MarketImpactSlippageModel(self));
security.set_slippage_model(MarketImpactSlippageModel(self))
The following table describes the arguments the model accepts:
| Argument | Data Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
algorithm | IAlgorithm | The algorithm instance | |
nonNegativenon_negative | bool | Indicator whether only non-negative slippage allowed. | trueTrue |
latency | doublefloat | Seconds between order submission and order fill | 0.075 |
impactTimeimpact_time | doublefloat | Seconds between order fill and the establishment of the new equilibrium | 1800 |
alpha | doublefloat | Exponent of the permanent impact function | 0.891 |
beta | doublefloat | Exponent of the temporary impact function | 0.600 |
gamma | doublefloat | Coefficient of the permanent impact function | 0.314 |
eta | doublefloat | Coefficient of the temporary impact function | 0.142 |
delta | doublefloat | Liquidity scaling factor for permanent impact | 0.267 |
randomSeedrandom_seed | int | Random seed for generating gaussian noise | 50 |
The default parameters of the MarketImpactSlippageModel are the parameters that the authors calibrated and shared. However, you may want to reference the original paper and recalibrate the parameters because of the following reasons:
- The default parameters are calibrated around 2 decades ago
- The trading time effect is not accounted (volume near market open/close is larger)
- The market environment does not have many market makers at that time
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.
For more information about this model, see the class reference and implementation.